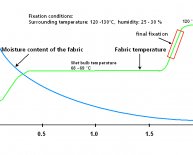
Wool dyeing process
 Phospholipids mixture from commercial soybean lecithin (SBL) was prepared as acetone insoluble fraction (AIF) which was acetylated at 70%. Phospholipids composition was elucidated with TLC-Densitometry. The acetylated AIF was used for preparing liposomes for encapsulating reactive dye for wool and wool blends dyeing. Ultrasonic irradiation was used in preparing liposomes. Particle size measurements of the liposomes encapsulating the dye at different concentrations were measured. Maximum particle size of about 16 nm was obtained at liposome concentration of 4 g/l.
Phospholipids mixture from commercial soybean lecithin (SBL) was prepared as acetone insoluble fraction (AIF) which was acetylated at 70%. Phospholipids composition was elucidated with TLC-Densitometry. The acetylated AIF was used for preparing liposomes for encapsulating reactive dye for wool and wool blends dyeing. Ultrasonic irradiation was used in preparing liposomes. Particle size measurements of the liposomes encapsulating the dye at different concentrations were measured. Maximum particle size of about 16 nm was obtained at liposome concentration of 4 g/l.
Dyeing was conducted under different parameters in presence and absence of microencapsulated (MS) dye. The colour strength values, exhaustion, levelling and fixation percent were higher in presence of liposome and tensoactive product than those of conventional dyeing process. These more satisfactory results of wool dyeing encouraged the application of the optimum conditions of wool dyeing on wool blend fabrics with efficiency dye uptake and levelling. Moreover, microencapsulation with liposomes as a new efficient technology for dyeing process prevents environmental pollution.
Keywords
- Soybean lecithin;
- Liposome vesicles;
- Nanoemulsion;
- Dyeing;
- Wool;
- Reactive dye